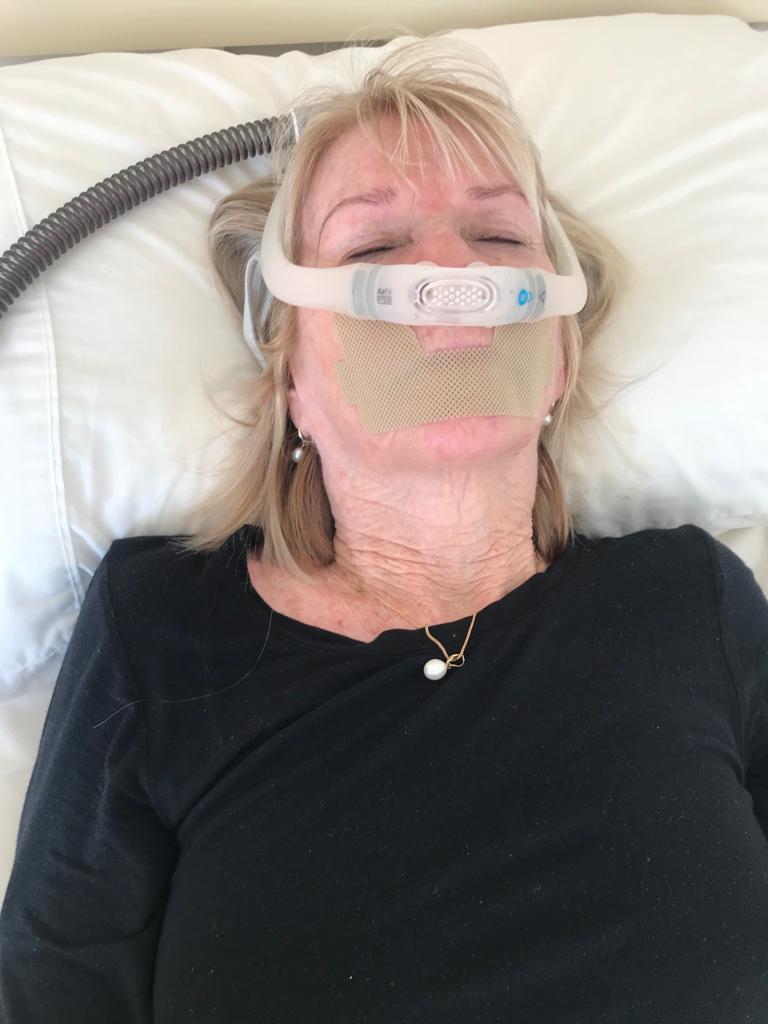
Stop snoring CPAP device:
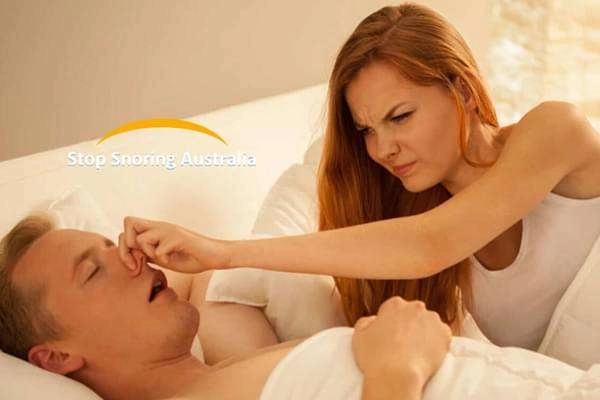
Snoring, often dismissed as a harmless annoyance, can be a disruptive and even debilitating issue for the snorer and their sleep partner. It can lead to sleep disruptions, strained relationships, and, in some cases, more severe health concerns. Thankfully, Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) devices have emerged as a highly effective solution to stop snoring and treat underlying sleep-related breathing disorders. This comprehensive article will explore the world of snoring, its causes, the significance of CPAP therapy, and the transformative impact of CPAP devices on sleep quality and overall health.
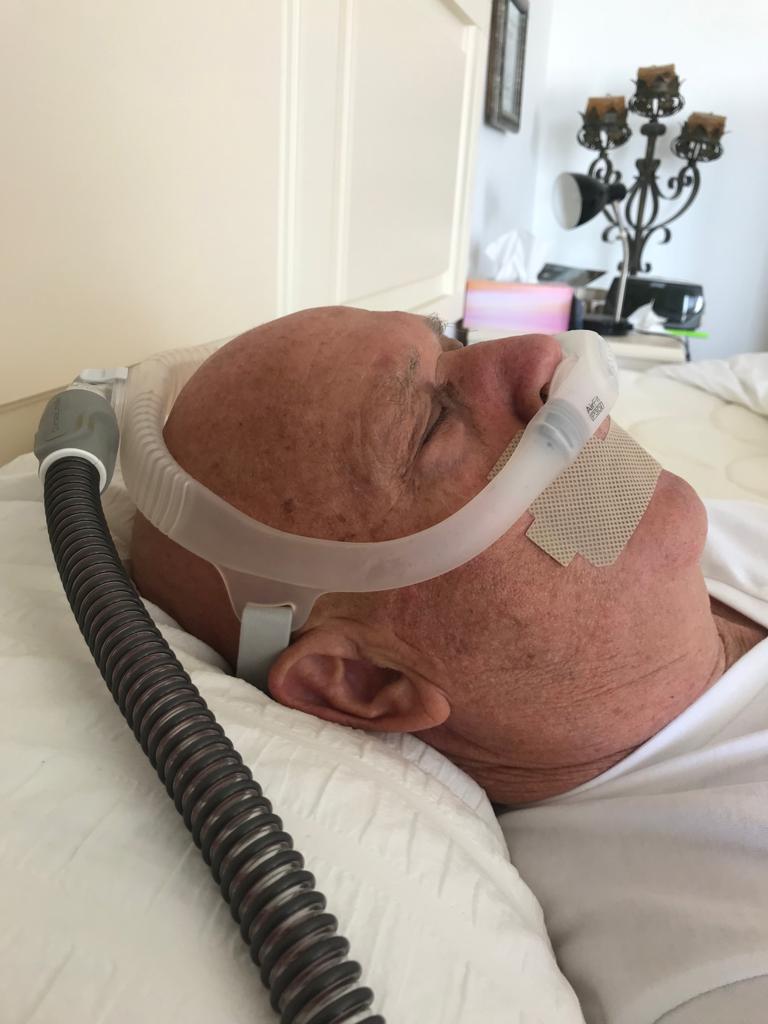
I. Understanding the Phenomenon of Snoring:
- What is Snoring? They were snoring results from turbulent airflow, causing soft tissues in the throat, particularly the uvula and the soft palate, to vibrate during sleep. It produces the sound of snoring, ranging from a soft, gentle murmur to a thunderous, disruptive noise.
- Prevalence and Impact: Snoring is common, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. It is estimated that approximately 45% of adults snore occasionally, while around 25% are habitual snorers. Snoring can lead to sleep disruptions for the snorer and their sleep partner, resulting in daytime fatigue, irritability, and, in severe cases, relationship strain.
II. The Causes of Snoring:
Understanding the causes of snoring is crucial in determining the most effective solutions. Snoring can be attributed to various factors:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): OSA is a severe sleep disorder characterized by repeated episodes of partial or complete upper airway obstruction during sleep. Loud snoring often accompanies it, leading to significant health risks if left untreated.
- Anatomy and Genetics: The structure of one’s airway and genetics can play a role in snoring. Some people have naturally narrower airways or anatomical variations predisposing them to snoring.
- Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle choices, such as excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, or obesity, can increase the likelihood of snoring. These factors can lead to relaxation of the throat muscles and contribute to snoring.
- Sleep Position: Sleeping on one’s back can promote snoring as the tongue and soft palate are more likely to collapse to the back of the throat, partially blocking the airway.
III. The Consequences of Chronic Snoring:
While snoring may be perceived as a mere inconvenience, it can have significant consequences, mainly when it is a symptom of a more severe condition like OSA. The repercussions of chronic snoring can include:
- Sleep Disruptions: Snoring can lead to fragmented sleep for the snorer and their sleep partner. These frequent awakenings prevent individuals from reaching the vital stages of deep sleep, resulting in daytime fatigue and impaired cognitive function.
- Daytime Fatigue and Impaired Performance: Persistent snoring can lead to excessive daytime sleepiness, making concentrating, focusing, and performing daily tasks difficult. It can impact work, relationships, and overall quality of life.
- Cardiovascular Risks: Often associated with loud snoring, OSA is linked to severe cardiovascular risks, including hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. The repeated pauses in breathing during sleep can strain the heart and lead to long-term health issues.
- Mental Health Implications: Chronic snoring and OSA have been associated with mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. The sleep disturbances and oxygen desaturation accompanying these conditions can negatively affect mental well-being.
- Relationship Strain: Snoring can strain relationships as the noise frequently disturbs sleep partners. It can lead to resentment, frustration, and even separate sleeping arrangements.
IV. The Role of CPAP Therapy:
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy has emerged as a gold standard in treating snoring and sleep-related breathing disorders, particularly OSA. CPAP devices deliver a constant stream of pressurized air through a mask, which keeps the airway open and prevents the collapse of soft tissues. However, in turn, it eliminates snoring and improves the quality of sleep.
- How CPAP Works:
- The CPAP device consists of a motor that generates air pressure, a hose to deliver the air, and a mask that covers the nose, mouth, or both.
- The pressurized air creates a pneumatic splint, preventing the airway from collapsing during sleep.
- By maintaining an open airway, CPAP therapy effectively treats snoring, OSA, and related symptoms.
Types of CPAP Masks:
CPAP masks come in various designs to accommodate individual preferences and comfort levels. These include:
- Nasal masks that cover the nose.
- Full-face shows that cover the nose and mouth.
- Nasal pillows that rest beneath the nostrils.
Choosing a suitable mask is essential for successful CPAP therapy.
The Impact of CPAP Therapy:
CPAP therapy can have a transformative impact on the lives of individuals with snoring and OSA:
- Improved Sleep Quality: CPAP therapy ensures uninterrupted breathing during sleep, leading to better sleep quality and more restorative rest.
- Elimination of Snoring: The pressurized air prevents the vibration of soft tissues, effectively eliminating snoring.
- Enhanced Daytime Function: With improved sleep, individuals experience increased energy, better concentration, and enhanced cognitive function during the day.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: CPAP therapy reduces the cardiovascular risks associated with OSA, lowering the chances of hypertension, heart disease, and stroke.
- Mood and Mental Well-being: Effective treatment of OSA can alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, improving overall mental health.
- Relationship Harmony: The elimination of snoring can significantly improve sleep partners’ quality of life, restoring harmony to relationships.
V. Overcoming Challenges with CPAP Therapy:
While CPAP therapy offers remarkable benefits, its successful implementation can sometimes be challenging. Addressing these challenges is essential to ensuring consistent and effective treatment:
- Mask Discomfort: Some individuals may initially find wearing a CPAP mask uncomfortable or claustrophobic. Proper mask selection and adjustments and patience can help overcome this issue.
- Mask Leaks: Leaks in shows can disrupt therapy and reduce its effectiveness. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent leaks, including cleaning and replacing mask components.
- Dryness and Congestion: The continuous airflow can lead to dryness in the nasal passages and throat. Humidification features in CPAP devices help alleviate this discomfort.
- Patient Compliance: Adhering to CPAP therapy consistently can be challenging for some individuals. Education, support, and ongoing monitoring by healthcare providers can encourage compliance.
VI. Exploring Advancements in CPAP Technology:
Advancements in technology have led to more user-friendly and efficient CPAP devices. Some of the notable developments include:
- Auto-Titrating CPAP (APAP): APAP devices automatically adjust the pressure based on the user’s needs throughout the night. This adaptive approach enhances comfort and optimizes therapy.
- BiPAP (Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure): BiPAP devices offer two distinct pressure settings—one for inhalation and a lower one for exhalation. It can be constructive for individuals who find standard CPAP pressure uncomfortable.
- Travel-Friendly CPAPs: Compact and lightweight CPAP devices are designed for travel, making it easier for users to maintain their therapy while on the go.
- Data Connectivity: Many CPAP devices now offer data connectivity, allowing users and healthcare providers to remotely monitor therapy adherence and effectiveness.
VII. A Holistic Approach to Sleep Health:
While CPAP therapy is highly effective for stopping snoring and treating sleep-related breathing disorders, a holistic approach to sleep health is essential. It includes:
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking can reduce the risk of snoring and sleep apnea.
- Positional Therapy: Positional therapy devices or techniques may benefit individuals whose snoring is primarily positional (i.e., worsens when sleeping on their back).
- Diet and Exercise: A well-balanced diet and regular exercise can contribute to overall health and improve sleep quality.
- Consulting a Healthcare Provider: Individuals experiencing chronic snoring or suspected sleep apnea should seek medical evaluation. A healthcare provider can conduct sleep studies and recommend appropriate treatments, including CPAP therapy.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, snoring is a common and often underestimated issue that can significantly affect sleep quality, health, and relationships. While there are various causes of snoring, including anatomical, lifestyle, and genetic factors, it is essential to address the underlying causes and choose appropriate treatment methods.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy has revolutionized the treatment of snoring and sleep-related breathing disorders, offering a path to silence the disruptive nocturnal symphony. CPAP devices, through the delivery of pressurized air, maintain an open airway, eliminate snoring, and promote restorative sleep.
The impact of CPAP therapy extends beyond the bedroom, improving overall health, cognitive function, and mood while reducing cardiovascular risks. However, successful CPAP therapy may require patience and adjustment to overcome initial challenges.
As technology advances, CPAP devices become more user-friendly, adaptive, and connected, making them even more accessible and practical. Combining CPAP therapy with a holistic approach to sleep health, including lifestyle modifications, can result in a more profound and enduring improvement in sleep quality and overall well-being.
In embracing the silence, individuals can transform their nights into restorative, peaceful journeys and awaken to brighter, more energized days. Through effective treatment, the disruptive melody of snoring can be replaced with the harmonious symphony of rejuvenating sleep.