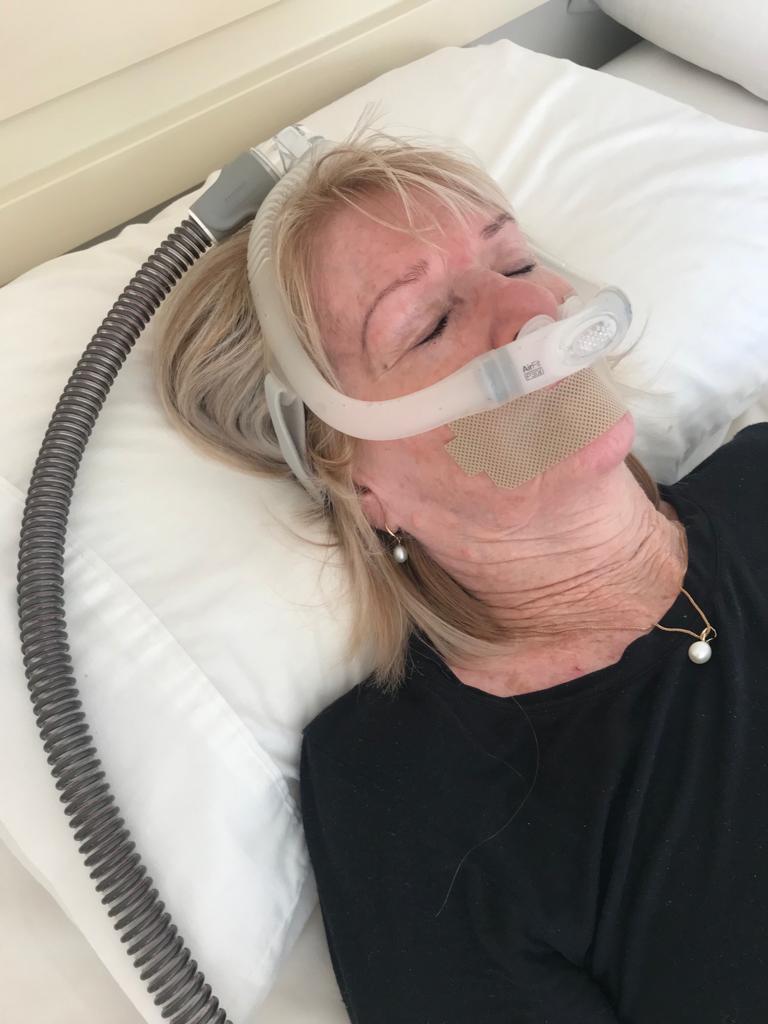
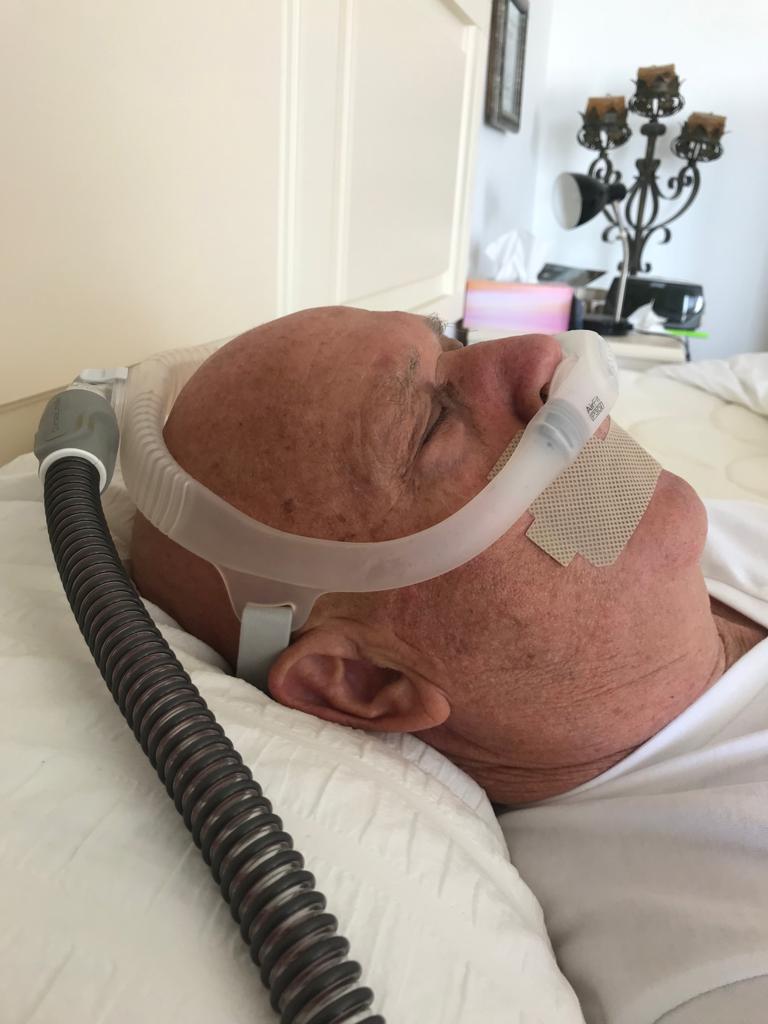
How to block out snoring:
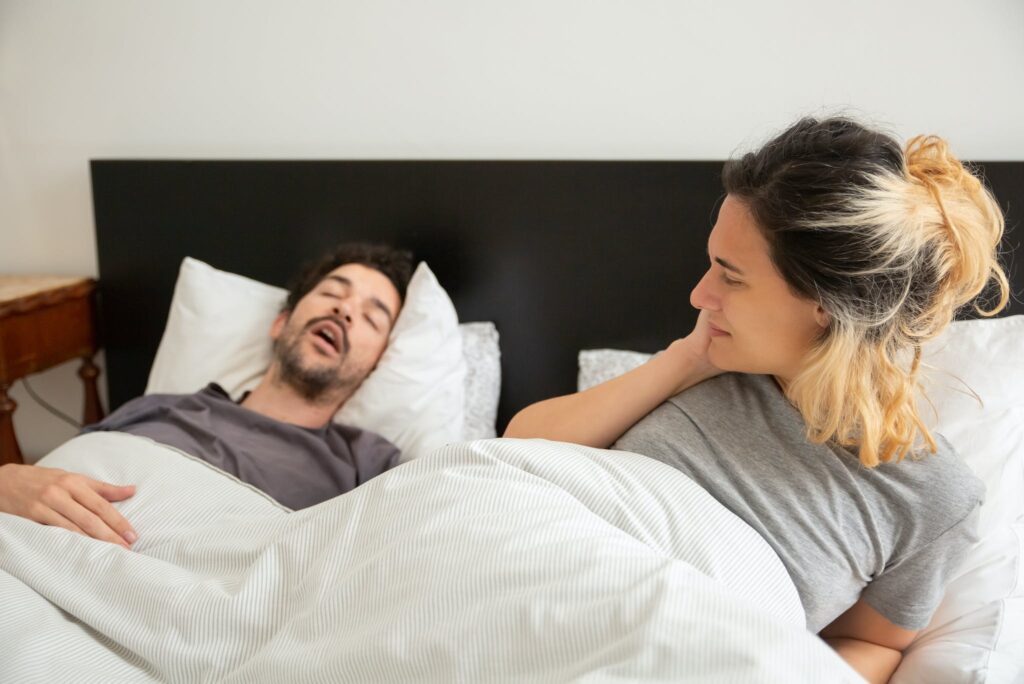
Sleep is a cornerstone of our overall health and well-being, and a peaceful night’s rest is essential for rejuvenation. However, for millions, sleep harmony is disrupted by the loud and persistent sound of snoring. Whether you’re the snorer or the sleep partner, the challenges of snoring can be frustrating and detrimental to the quality of your rest. This comprehensive guide will explore effective strategies and practical solutions to block snoring, ensuring you and your loved ones can sleep a restful night. You can also visit The British Snoring and Sleep Apnoea Association
I. Understanding the Basics of Snoring
Before we delve into how to block out snoring, it’s crucial to understand what snoring is and why it occurs.
What is Snoring?
The snoring results from vibrations in the upper airway caused by the turbulent airflow during sleep. These vibrations produce snoring, ranging from soft, gentle purring to loud, disruptive noises.
Common Causes of Snoring:
- Anatomy: The physical structure of the throat and nasal passages can play a significant role in snoring. Factors like a deviated septum, enlarged tonsils, or obesity can lead to snoring.
- Sleep Position: Sleeping on your back often increases the likelihood of snoring as it can cause the tongue and soft palate to collapse to the back of the throat, partially obstructing the airway.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and sedative medications can relax the muscles in the throat, making snoring more likely.

II. Addressing the Causes of Snoring:
To effectively block out snoring, addressing its underlying causes is essential. Here are some strategies for identifying and mitigating these factors:
Consult a Healthcare Provider:
Snoring may indicate an underlying sleep disorder like sleep apnea if snoring is persistent and disruptive. Consulting a healthcare provider is the first step in determining the cause of snoring and receiving appropriate treatment.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight Management: For individuals who are overweight, losing excess weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can reduce the risk of snoring.
- Limit Alcohol and Sedatives: Reducing alcohol consumption and avoiding sedative medications, especially in the evening, can help prevent muscle relaxation in the throat.
Sleep Position:
- Positional Therapy: For snorers whose snoring is primarily positional (worsening when sleeping on the back), positional therapy devices, like special pillows or wearable devices, can help encourage side-sleeping.
Allergen Control:
- Allergies and Nasal Congestion: Allergies and nasal congestion can contribute to snoring. Managing allergies through medications or lifestyle changes and using saline nasal sprays can alleviate congestion and reduce snoring.
III. Lifestyle Changes for the Snorer:
If you are the one who snores, making specific lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the severity and frequency of your snoring:
- Quit Smoking: Smoking irritates and inflames the tissues in your throat and nasal passages, contributing to snoring. Quitting smoking can have numerous health benefits, including reduced snoring.
- Alcohol and Sleep: Avoid consuming alcohol for at least four to six hours before bedtime. Alcohol relaxes the throat muscles, making snoring more likely.
- Diet and Exercise: Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity. Excess weight, particularly around the neck, can contribute to snoring.
- Hydration: Stay well-hydrated throughout the day, but avoid excessive fluid intake in the evening to reduce the risk of nighttime bathroom trips, which can disrupt sleep and lead to snoring.
- Sleep Hygiene: Establish a regular sleep routine and prioritize good sleep hygiene practices, such as going to bed and waking up at the same time daily and creating a comfortable sleep environment.
IV. Devices and Products to Block Out Snoring:
Various devices and products are available to help individuals and sleep partners block out snoring effectively:
Anti-Snoring Pillows:
- Anti-snoring pillows are designed to encourage side sleeping and maintain proper head and neck alignment. Some also incorporate features like built-in speakers that emit positional cues when snoring is detected.
Nasal Strips and Dilators:
- Nasal strips and dilators improve airflow through the nasal passages, reducing the likelihood of mouth breathing and snoring.
Mouthpieces and Mandibular Advancement Devices (MADs):
- MADs are worn in the mouth and work by repositioning the lower jaw and tongue to keep the airway open during sleep. However, it is often effective for mild to moderate snoring.
Anti-snoring rings and Bracelets:
- These devices are designed to apply pressure to specific acupressure points on the fingers or wrists, promoting relaxation and improved airflow. Their effectiveness varies from person to person.
Smartphone Apps:
- Several smartphone apps are designed to detect and record snoring sounds. They can be used for self-monitoring or to gather data for healthcare providers.
V. Medical and Dental Solutions:
Medical and dental solutions may be necessary for individuals with persistent or severe snoring. These options should be explored in consultation with a healthcare provider:
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP):
- CPAP devices are the gold standard in treating snoring and sleep apnea. They deliver a continuous stream of pressurized air through a mask, preventing the airway from collapsing during sleep.
Oral Appliances:
- Dental appliances, such as Mandibular Advancement Devices (MADs) or tongue-retaining devices, can be prescribed by a dentist to help reposition the jaw and tongue to keep the airway open.
Surgical Interventions:
- Surgical interventions, such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP), may address anatomical issues contributing to snoring in cases where other treatments are ineffective or contraindicated.
Positional Therapy Devices:
- Specialized devices worn during sleep can help encourage side-sleeping, reducing the severity of snoring for those whose snoring is primarily positional.
VI. The Importance of Seeking Professional Help:
Persistent or severe snoring may indicate an underlying sleep disorder like sleep apnea, which can have profound health implications. If snoring disrupts your sleep or your partner’s sleep, it is crucial to seek professional help. A healthcare provider or sleep specialist can conduct a thorough evaluation, including sleep studies, to determine the cause of snoring and recommend appropriate treatment options.
VII. A Restful Night’s Sleep is Within Reach:
Snoring can disrupt the tranquility of sleep for the snorer and their sleep partner, leading to fatigue, irritability, and strained relationships. However, with the right strategies and solutions, you can block out snoring and reclaim the restful nights you deserve.
From lifestyle modifications and devices designed to reduce snoring to medical and dental interventions, numerous options are available to address snoring effectively. Identifying the underlying causes and tailoring your approach to your unique situation is vital.
Remember that seeking professional help is essential if snoring persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms. By taking proactive steps to address snoring, you can enjoy a more peaceful and rejuvenating night’s sleep, ultimately contributing to your overall health and well-being.